Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold: A Comprehensive Guide
catalyst system efficiency below threshold is a crucial aspect of modern vehicles, particularly in managing emissions and ensuring environmental compliance. When the warning pops up, it typically indicates that something is wrong with your vehicle’s catalytic converter. This is more than just a technical issue—it’s a significant concern for drivers, as it can lead to poor performance, increased emissions, and even hefty fines in regions with catalyst system efficiency below threshold strict emission laws.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into what this error means, why it occurs, how to diagnose it, and possible solutions. Whether you’re a car enthusiast or someone just trying to understand the lights on your dashboard, this guide is designed to give you the full picture.
What Does “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold” Mean?
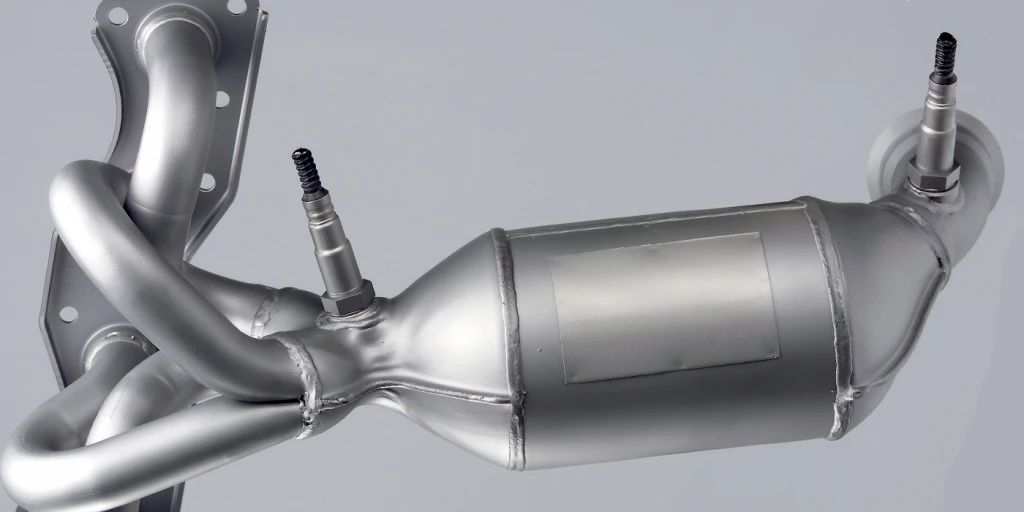

The “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold” warning typically refers to a problem with your vehicle’s catalytic converter. This component is part of your car’s exhaust system, designed to reduce harmful emissions like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides by converting them into less harmful substances before they exit the exhaust.
How the Catalytic Converter Works
At its core, the catalytic converter uses a combination of precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium to trigger chemical reactions that neutralize catalyst system efficiency below threshold harmful gases. When functioning properly, this component ensures that your vehicle meets emission standards by cleaning up the exhaust before it leaves your car.
The Role of Oxygen Sensors
The oxygen (O2) sensors, typically one placed before and one after the catalytic converter, play a significant role in monitoring its efficiency. The sensors track the amount of oxygen in the exhaust and feed that information to the car’s engine control module (ECM). If the ECM detects a discrepancy in the readings—specifically, if the post-converter sensor shows higher levels of harmful gases—it triggers the “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold” code (usually P0420 or P0430).
What the Warning Actually Means
The warning essentially tells you that the catalytic converter is no longer performing as efficiently as it should. This doesn’t always mean it’s broken, but it could be clogged, damaged, or simply worn out after years of use. Ignoring this issue can lead to worse fuel economy, increased emissions, and possible engine damage.
Common Causes of Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
There are several reasons why this error message may appear. Understanding the causes is key to diagnosing the problem correctly and taking appropriate action.
Age and Wear
Catalytic converters have a finite lifespan. Over time, the metals inside the converter can degrade, reducing its ability to facilitate the chemical reactions that neutralize emissions. This is particularly common in older vehicles with high mileage. If your car has been on the road for more than a decade, the “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold” warning may be simply due to age.
Faulty Oxygen Sensors
Sometimes, the catalytic converter itself isn’t the problem—the issue lies with the O2 sensors. These sensors play a critical role in monitoring the exhaust gases. catalyst system efficiency below threshold If they become faulty, dirty, or damaged, they can give incorrect readings to the ECM, which may lead to a false catalyst efficiency warning. Replacing the O2 sensors is often a simple and cost-effective solution.
Exhaust Leaks
Leaks in your exhaust system can also trigger this warning. If exhaust gases are escaping before they reach the catalytic converter, the O2 sensors may detect less oxygen than is actually present, causing the ECM to flag a potential efficiency issue. Common sources of leaks include the exhaust manifold, gaskets, or even the catalytic converter itself.
Contamination
The catalytic converter can become contaminated by catalyst system efficiency below threshold substances such as oil, coolant, or unburned fuel. This contamination can coat the catalyst, preventing it from doing its job properly. Oil leaks from worn valve seals, head gaskets, or piston rings can cause this type of contamination. If fuel injectors are malfunctioning, unburned fuel can enter the exhaust system, further complicating matters.
Misfires and Rich/Lean Air-Fuel Mixture
Misfires, or an improper air-fuel mixture (running too rich or too lean), can also reduce catalytic converter efficiency. A rich mixture means there’s too much fuel and not enough air, which can overwhelm the converter. A lean mixture, on the other hand, means there’s too much air and not enough fuel, resulting in inefficient combustion and poor converter performance.
Diagnosing Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
Diagnosing the “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold” error involves a combination of visual inspections, tests, and data analysis. It’s essential to identify whether the catalytic converter itself is the problem or if something else is causing the error.
Scan for Trouble Codes
The first step is to connect an OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics) scanner to your car’s diagnostic port. The code most commonly associated with this issue is P0420 catalyst system efficiency below threshold (for Bank 1) or P0430 (for Bank 2). These codes will give you a starting point for further investigation.
Inspect the Oxygen Sensors
Since faulty O2 sensors can cause this issue, they should be one of the first components you inspect. If the sensors are covered in soot, carbon deposits, or appear damaged, they may be malfunctioning. O2 sensors can be tested using a multimeter to check the voltage output or with a professional diagnostic tool.
Check for Exhaust Leaks
A thorough inspection of your exhaust system for leaks is crucial. Look for any cracks, holes, or damaged gaskets in the exhaust manifold, pipes, or catalytic converter. catalyst system efficiency below threshold Even a small leak can lead to incorrect sensor readings.
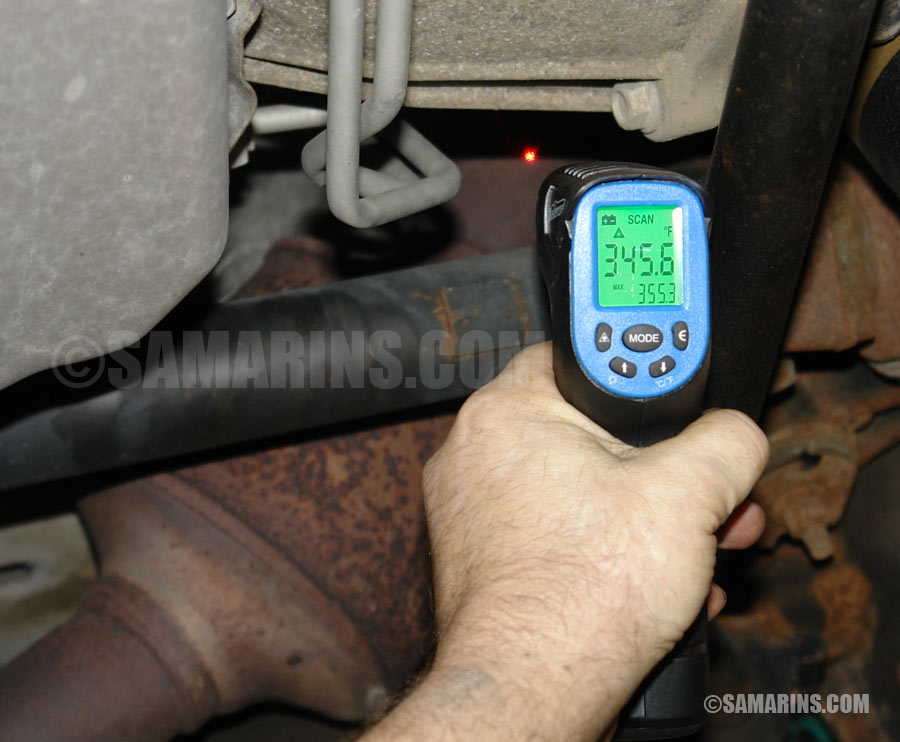
Perform a Catalytic Converter Test
To test the catalytic converter, a backpressure test can be performed. If the converter is clogged, it will cause an increase in backpressure, which can be measured using specialized tools. Additionally, a temperature test can be conducted by measuring the temperature at both ends of the converter. If the temperature difference is minimal, it may indicate that the converter is not functioning properly.
How to Fix Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
Once you’ve diagnosed the issue, it’s time to take action. Depending on the root cause, there are several solutions available.
Replace Faulty Oxygen Sensors
If the O2 sensors are at fault, replacing them can often resolve the issue. This is one of the simpler and more affordable fixes, as O2 sensors are relatively inexpensive and catalyst system efficiency below threshold can be replaced without too much labor. Make sure to use high-quality sensors to avoid future problems.
Repair Exhaust Leaks
If leaks are detected in the exhaust system, they should be repaired immediately. Depending on the location of the leak, this could involve replacing gaskets, welding cracks, or installing new exhaust pipes. Fixing the leaks will ensure that the catalytic converter receives the correct amount of exhaust gases, improving its efficiency.
Clean or Replace the Catalytic Converter
In some cases, cleaning the catalytic converter may restore its functionality. There are commercial catalytic converter cleaners available that can help remove carbon catalyst system efficiency below threshold deposits or other contaminants. However, if the converter is severely damaged or clogged, replacement is the only viable option. Replacing a catalytic converter can be expensive, but it’s essential for maintaining vehicle performance and reducing emissions.
Address Engine Misfires and Air-Fuel Ratio Issues
If the problem stems from engine misfires or an incorrect air-fuel ratio, these issues must be addressed to protect the catalytic converter. This may involve replacing spark plugs, fuel injectors, or even performing a full engine tune-up. Ensuring that your engine is running smoothly will prevent future damage to the catalytic converter.
Preventing Catalyst System Efficiency Issues
Preventative maintenance is key to avoiding catalyst efficiency problems. By taking care of your vehicle, you can prolong the life of the catalytic converter and prevent the dreaded “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold” warning.
Regular Maintenance
One of the best ways to prevent catalytic converter issues is by staying on top of regular vehicle maintenance. This includes oil changes, air filter replacements, and catalyst system efficiency below threshold scheduled tune-ups. Keeping the engine in good condition reduces the risk of contaminants entering the exhaust system and damaging the catalytic converter.
Monitor Fuel Quality
Using high-quality fuel can also make a difference. Cheap, low-grade fuel may contain impurities that can clog the catalytic converter over time. Additionally, avoid driving with catalyst system efficiency below threshold a low fuel level, as this can cause the fuel pump to pick up dirt or sediment from the bottom of the fuel tank, which can end up in the catalytic converter.
Address Check Engine Lights Promptly
Many drivers ignore the “Check Engine” light for as long as possible, but this is a mistake. Early detection of problems can prevent them from becoming more severe. If the “Check Engine” light is related to the catalytic converter or O2 sensors, addressing the issue quickly can save you from costly repairs down the line.
Legal and Environmental Implications
Ignoring catalyst efficiency problems can have both legal and environmental consequences. In many regions, vehicles are required to pass emission tests to be legally catalyst system efficiency below threshold driven on the road. Failing these tests can result in fines, revoked registration, or being forced to make expensive repairs.
Emission Tests
Catalytic converters play a significant role in ensuring that vehicles comply with emissions standards. If your car’s converter is not functioning properly, it’s likely that your vehicle will fail its emission test. This could prevent you from registering your vehicle, or worse, result in fines and penalties.
Environmental Impact
Beyond the legal ramifications, a failing catalytic converter can have a substantial environmental impact. Without it, harmful gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides can escape into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and smog. Responsible car ownership includes maintaining your vehicle’s emission control systems to help protect the environment.
When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
While some issues can be resolved by DIY enthusiasts, others require professional intervention. If you’re unsure about the cause of the “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold” warning, or if attempts to fix it haven’t been successful, it’s best to consult a certified mechanic.
What to Expect from a Mechanic
A professional mechanic will typically perform a comprehensive diagnostic check using advanced tools. They’ll inspect the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, exhaust catalyst system efficiency below threshold system, and engine to identify the root cause of the problem. Depending on the findings, they can recommend the most appropriate course of action, whether that involves repairs or replacements.
Cost Considerations
Repairing or replacing a catalytic converter can be expensive. Depending on the make and model of your vehicle, a new converter can cost anywhere from $200 to over $2,000, not including labor. If budget is a concern, consider consulting multiple mechanics for estimates or exploring options for refurbished parts.
Conclusion
The “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold” warning is not something to be ignored. While it may be an indication of a minor issue, such as a faulty oxygen sensor, it could also point to more severe problems like a failing catalytic converter. Understanding what causes this error, how to diagnose it, and the available solutions can save you time, money, and a lot of frustration.
By following the tips outlined in this article, you can address the catalyst system efficiency below threshold problem head-on and ensure that your vehicle continues to run efficiently and cleanly. Regular maintenance, prompt repairs, and attention to detail can go a long way in preventing catalytic converter issues.







Post Comment